Nitrous oxide is a safe and effective option for managing postpartum pain and anxiety while breastfeeding. You’ll find it clears from your system within 3-5 minutes, with minimal transfer to breast milk and no need to pump and dump. Research shows it can improve mental wellness by triggering dopamine release and reducing anxiety, while preserving your mobility and ability to nurse. When administered as a 50/50 mixture with oxygen under medical supervision, it provides evidence-based benefits that support your postpartum experience.
Understanding Nitrous Oxide Safety in Labor and Breastfeeding

While nitrous oxide has emerged as a valuable pain management option during labor, its safety profile extends to postpartum care and breastfeeding. You’ll find that it provides effective pain relief without compromising maternal consciousness or inhibiting your ability to actively participate in the birthing process. Nitric oxide naturally plays a role in milk letdown reflex, making it compatible with normal lactation processes. The 50/50 gas mixture is delivered through a specialized system designed specifically for labor and delivery use. Recent data shows 40 to 60 percent of women initially using nitrous oxide later switch to epidural analgesia for more effective pain control.
The rapid clearance of nitrous oxide from your system (within 3-5 minutes) and its minimal accumulation in blood and fat make it particularly compatible with breastfeeding. Despite clear anesthesia contraindications for mothers with B12 deficiency or those requiring supplemental oxygen, research supports its safety when properly administered. While short-term safety data is sturdy, long term outcomes monitoring remains an area requiring further study. You won’t need to pump and dump breastmilk after nitrous oxide use, as studies show no detectable transfer through breastmilk after discontinuation.
Mental Health Benefits for New Mothers
Beyond its physical pain management benefits, nitrous oxide offers significant mental health advantages for new mothers traversing the postpartum period. This intervention plays an essential role in enhancing mood stability by triggering dopamine release and inhibiting anxiety-inducing neurotransmitters during labor, potentially reducing your risk of postpartum mental health challenges. Mood symptoms typically emerge within the first few postpartum weeks.
You’ll find that nitrous oxide’s self-regulated administration helps in reducing anxiety related distress, as you maintain control over your pain management. The 50/50 mixture administered through a mask provides a consistent and reliable dosage for optimal results. Research indicates that effective pain relief during labor correlates with better postpartum outcomes, particularly since 50-80% of new mothers experience baby blues and 1 in 7 develop postpartum depression. By altering pain perception and minimizing acute fear responses, nitrous oxide creates a more positive birth experience that may help protect against subsequent anxiety and depression symptoms. Since anxiety disorders often coexist with postpartum depression, addressing both conditions early through effective interventions is crucial for maternal wellbeing.
Best Practices for Administration During Recovery
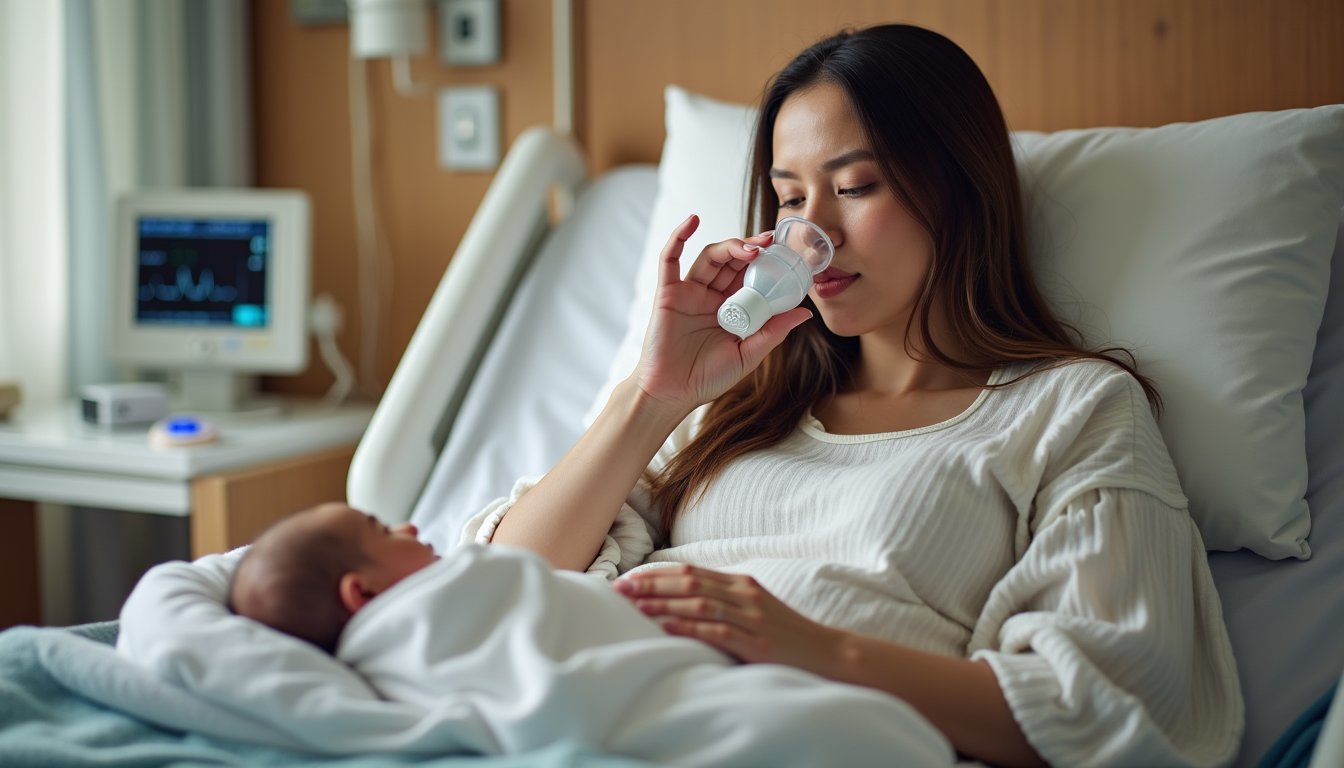

Consistently implementing proper administration protocols guarantees safe and effective nitrous oxide use during postpartum recovery. Due to its half-life under 3 minutes, nitrous oxide clears rapidly from your system after discontinuation. You’ll self-administer a 50/50 mixture of nitrous oxide and oxygen through a facemask, maintaining control over your dosing while preserving postpartum mobility.
Your healthcare team will conduct thorough side effect monitoring, checking for nausea, dizziness, or oxygen desaturation throughout the recovery period. Once you’ve fully recovered from the anesthesia effects, you can safely resume breastfeeding. They’ll assess your readiness to move to alternative pain management methods, such as NSAIDs, while providing clear guidance on wound care if you’ve undergone procedures like episiotomies. You’ll receive specific instructions about recognizing potential complications and medication interactions before discharge.
Evidence-Based Research on Maternal Outcomes
Research demonstrates compelling evidence for nitrous oxide’s positive impact on maternal outcomes during postpartum recovery. The case-control study included 62 women who used nitrous oxide compared to 124 controls. Studies show improved postpartum experiences with higher breastfeeding success rates at key milestones and enhanced maternal satisfaction during physical recovery. You’ll find that 90% of users report high labor satisfaction memories, while 83.5% indicate positive pain relief experiences. The use of 50% N2O with oxygen ensures optimal safety while providing effective pain management. Women maintain full mobility during labor, allowing them to move freely before deciding on other pain management options.
Clinical studies reveal nitrous oxide enhances maternal satisfaction and breastfeeding success while providing effective pain management during postpartum recovery.
Key evidence-based findings include:
- Markedly higher breastfeeding rates at 7 days (p < 0.031), 1st month (p < 0.043), and 3rd month postpartum (p < 0.016)
- Rapid metabolization ensuring minimal breast milk transfer and reinforced postpartum physical recovery
- No considerable adverse effects on maternal mental health or milk production
These outcomes support nitrous oxide’s role in promoting successful postpartum adaptation while maintaining ideal safety profiles for both mother and infant.
Comparing Pain Management Options for Nursing Mothers

Nursing mothers require informed choices about pain management methods that align with their breastfeeding goals. You’ll find both pharmacological and non-pharmacological options available, with varying levels of compatibility with breastfeeding techniques. Studies show that self-management interventions effectively reduce discomfort while maintaining ideal feeding practices. Research demonstrates that mothers who receive pain self-management strategies report significantly lower pain intensity during breastfeeding. Recent evidence confirms that skin-to-skin contact provides natural pain relief benefits through multiple physiological mechanisms. The ability to remain fully mobile and controlled while using nitrous oxide makes it an attractive option for nursing mothers.
| Pain Management | Safety Profile | Medication Interactions |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrous Oxide | High | Minimal |
| NSAIDs | Moderate | Consider timing |
| Opioids | Variable | Requires monitoring |
Your options include evidence-based approaches like breathing exercises, cognitive reframing, and social support networks that don’t interfere with lactation. When medication becomes necessary, nitrous oxide offers anxiety and pain relief without motor impairment. You’ll want to carefully weigh the benefits and risks of stronger analgesics, particularly regarding their potential impact on milk production and infant safety.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Nitrous Oxide Affect My Baby’s Sleep Patterns While Breastfeeding?
Research hasn’t shown any direct link between nitrous oxide and your baby’s sleep patterns through breastfeeding. The gas clears from your system within minutes and doesn’t affect breastmilk composition. No breathing pattern changes have been observed in breastfed infants whose mothers received nitrous oxide. You can feel confident that this medication won’t disrupt your baby’s sleep, as it doesn’t accumulate in breast milk or cause lasting effects.
How Long Should I Wait Between Nitrous Oxide Sessions During Postpartum Recovery?
You’ll need to work with your healthcare provider to determine proper dosage guidelines and appropriate frequency between sessions, as there’s no fixed waiting period. Your individual health status, pain levels, and recovery progress will guide timing. Generally, you can use nitrous oxide as needed for acute symptoms since it’s rapidly eliminated from your system within minutes. Always follow your provider’s specific recommendations for your postpartum recovery plan.
Will Nitrous Oxide Interact With My Postpartum Depression Medications?
You’ll need to discuss potential medication interactions with your healthcare provider, as nitrous oxide can interact with several postpartum depression medications. It’s especially crucial to be cautious with benzodiazepines and medications affecting NMDA receptors. These combinations may increase sedation risks and impact mental health stability. Your doctor should evaluate your specific medication regimen, as individual responses vary based on genetic factors and your psychiatric history.
Does Nitrous Oxide Use Impact Milk Production or Letdown Reflex?
Current research shows no evidence that nitrous oxide directly impacts milk production or letdown reflex when used for pain management. You won’t experience decreased milk supply or inhibited letdown from proper nitrous oxide use. The medication’s rapid clearance from your system (within minutes) means it doesn’t accumulate in breast milk. Supplementally, the mental relaxation effects can actually support successful breastfeeding by reducing stress and anxiety during nursing sessions.
Can I Use Nitrous Oxide While Co-Sleeping With My Nursing Infant?
While nitrous oxide safety is generally established for breastfeeding mothers, you shouldn’t use it while co-sleeping with your infant. Despite maintaining alertness, it’s best to separate nitrous oxide use from sleep periods to guarantee maximum safety. If you’re facing breastfeeding challenges that require pain management, consider using nitrous oxide during awake nursing sessions only, and always consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance on timing and dosage.