You’ll need to follow a multi-tiered maintenance schedule for nitrous oxide equipment in mental health settings. Perform daily safety checks of connections, hoses, and fail-safe mechanisms. Complete weekly calibrations and seal inspections, followed by monthly performance evaluations of pressure systems. Schedule quarterly compliance audits to verify documentation and storage standards. Annual certifications must align with FDA and USP requirements. Proper maintenance protocols guarantee excellent patient care while meeting critical safety regulations.
Daily Safety Checks and Equipment Inspection Requirements
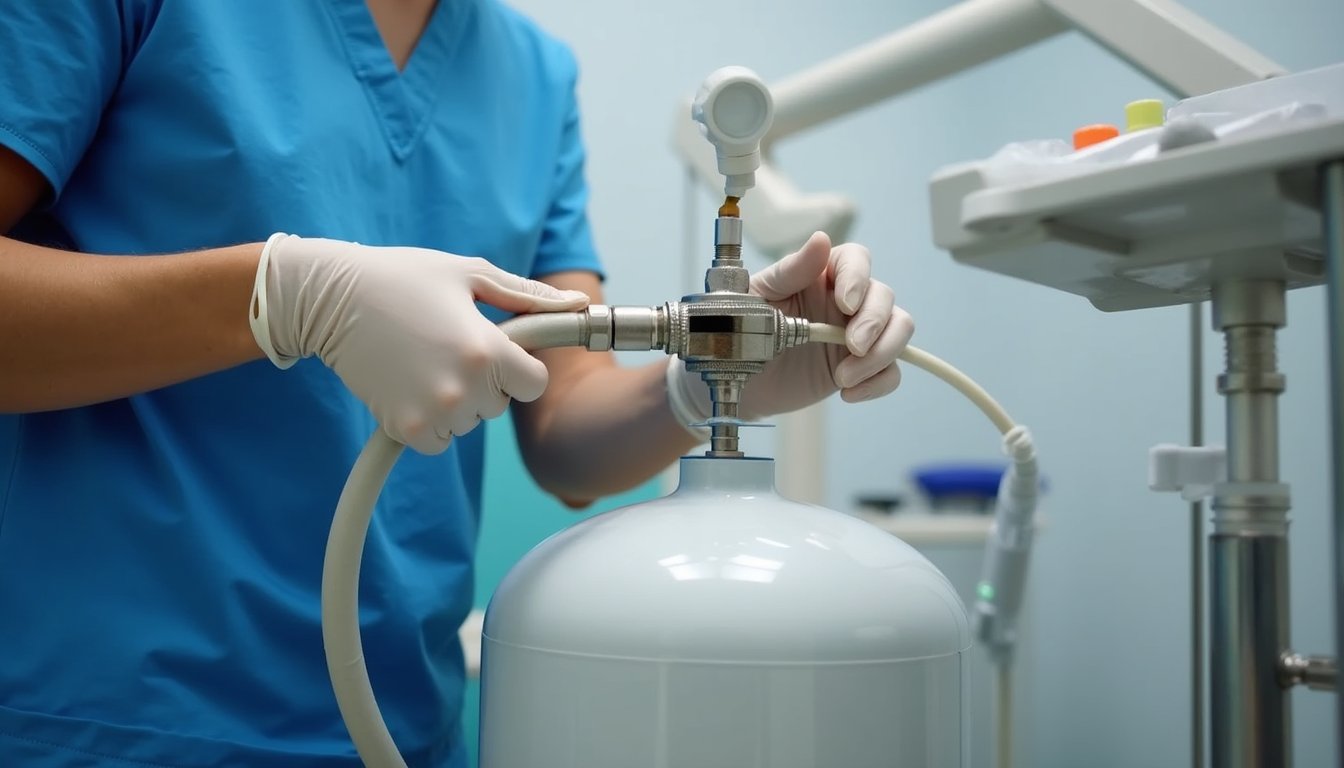
Dental professionals must conduct thorough daily safety inspections of nitrous oxide delivery systems to guarantee patient and staff safety. Start each day by verifying secure connections between hoses, regulators, and masks while testing the fail-safe mechanism that prevents nitrous oxide flow without adequate oxygen levels. Check gas cylinder volumes and proper storage orientation, then validate the scavenger system’s functionality to prevent ambient gas accumulation. Following proper instructions for use from manufacturers is essential for maintaining equipment safety and federal compliance.
Exposure monitoring protocols require consistent badge deployment to track ambient levels against OSHA’s 25 ppm threshold. Document all inspection findings in equipment logs and report any exceedances immediately. Scavenger system optimization involves testing vacuum pressure, examining hose integrity, and confirming proper ventilation connections. Replace damaged components immediately rather than attempting repairs to maintain system integrity and compliance with safety standards.
Weekly Maintenance and Calibration Schedules
While daily checks establish baseline safety, weekly maintenance procedures require a more thorough approach to nitrous oxide system optimization. Your preventative maintenance protocols should include inspecting gas supply lines for leaks, verifying pressure gauge readings against manufacturer specifications, and replacing worn o-rings or seals on connectors. At this time, perform checks on rubber goods on analgesia systems to ensure safety and functionality. Spore testing should be conducted according to proper sterilization protocols. Regular maintenance helps extend equipment lifespan while minimizing unexpected failures.
You’ll need to flush delivery units with approved cleaning solutions and test gas flow rates using calibrated instruments. Staff training requirements mandate that team members understand proper cleaning of vacuum lines and decontamination of surrounding surfaces. Track usage hours diligently to determine when components need replacement. Document all calibrations and adjustments in maintenance logs, and coordinate with vacuum system maintenance schedules to minimize disruptions. Remember to test emergency shut-off mechanisms during your weekly inspections to guarantee optimal system performance.
Monthly System Performance Evaluations
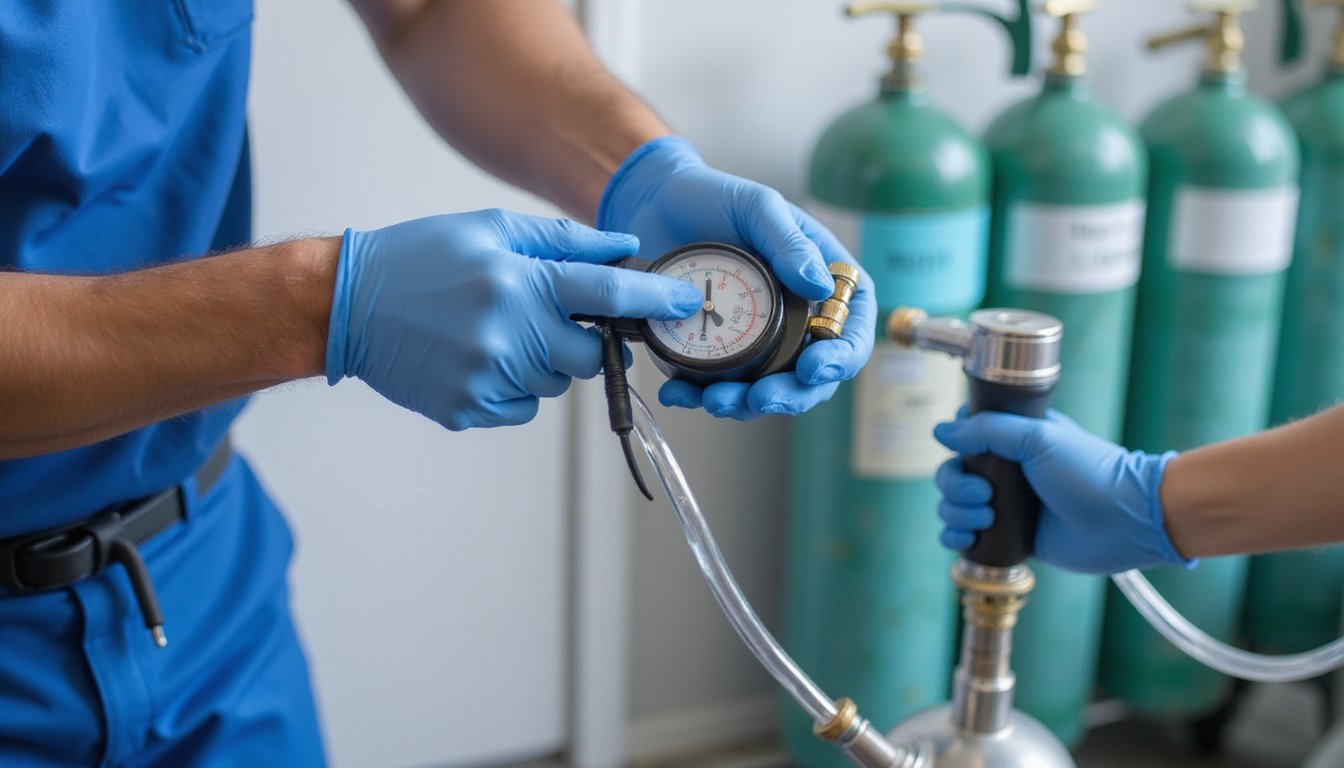

Building upon weekly maintenance protocols, monthly system performance evaluations demand an extensive technical assessment of your nitrous oxide delivery infrastructure. You’ll need to perform pressure transducer calibration alongside thorough leak detection using infrared spectrophotometers to identify potential gas escape points.
Your preventive maintenance protocols should include validating vacuum pump performance against manufacturer specifications, ensuring flow rates meet the 45 liters/minute requirement per workstation. Test all connections and valves for structural integrity while verifying proper exhaust system function. Cross-reference your flow data with ACGIH/OSHA exposure limits (25-50 ppm TWA) to maintain compliance.
Document all maintenance actions with equipment ID numbers and maintain calibration certificates with date-stamped logs. Monitor humidity levels and conduct IR spectroscopy instrument validation within 12.5-500 ppm ranges.
Quarterly Compliance Audits and Documentation Reviews
To maintain regulatory compliance and system integrity, quarterly audits require thorough reviews across multiple documentation streams and physical inspections. You’ll need to coordinate with suppliers to conduct cylinder inventory audits, ensuring physical holdings match movement records and commercial agreements. Proper segregation of full and empty cylinders using designated labeling systems must be verified during each quarterly review.
During these reviews, you must verify storage area compliance with temperature thresholds below 25°C and proper ventilation standards. Your documentation checks should encompass maintenance logs detailing pressure tests, leak checks, and equipment repairs. Cross-reference these against safety inspection records for valves, regulators, and connections.
Align your quarterly evaluations with NIH-defined intervals while adhering to EIGA Doc 33, ISO 23208, and NFPA99 standards. Remember to maintain all audit reports and reconciliation documents for a minimum of two years to satisfy regulatory requirements.
Annual Equipment Certification and Replacement Guidelines

Beyond quarterly audits, annual equipment certification demands rigorous adherence to FDA 21 CFR 211 standards and USP purity requirements. Your facility’s record retrieval procedures must demonstrate comprehensive cylinder storage management and compliance with NFPA 99 specifications. Maintaining consistent temperature at 21°C ensures optimal gas delivery and equipment performance. The medical-grade cylinders require fixed rack mounting to prevent contamination and ensure proper storage integrity.
- Validate third-party certifications and maintain batch record documentation showing ≥99.99% purity levels
- Complete annual pressure gauge calibration and flow meter recalibration for precise delivery monitoring
- Perform residual gas analysis and impurity threshold testing through validated gas chromatography
- Update storage history logs with temperature records and ventilation system performance data
- Guarantee staff maintains current OSHA chemical handling certifications and emergency protocol training
You’ll need to schedule manufacturer-specific inspections and maintain detailed QA/QC records demonstrating compliance with USP standards and FDA regulations throughout your supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Happens if Emergency Maintenance Is Needed During an Active Patient Session?
When emergency maintenance is needed during an active session, you’ll need to immediately activate patient safety protocols. Initial, halt the N₂O administration and stabilize your patient. You’ll trigger the automated alert system if equipment malfunction procedures detect issues. Activate scavenger systems and evacuation protocols if gas levels exceed thresholds. Your emergency response team will secure the equipment while maintaining patient care until the system is fully contained and cleared.
How Long Can Unused Nitrous Oxide Cylinders Be Safely Stored?
Under proper storage conditions, you can safely store nitrous oxide cylinders for up to 30 years if they’re made of seamless steel or aluminum. However, you’ll need to maintain strict environmental controls: keep cylinders upright in cool, dry, well-ventilated areas away from direct sunlight. You should regularly inspect for damage, monitor cylinder expiration dates, and check for signs of spoilage like unusual odors or pressure changes. Replace cylinders immediately if you notice dents, rust, or valve issues.
Can Equipment From Different Manufacturers Be Used in the Same System?
While you can mix equipment from different manufacturers, you’ll need to guarantee full compatibility between components. Focus on matching standardized connectors, pressure regulations, and flow specifications. You should verify that compatible equipment models meet universal fit requirements for accessories like nasal hoods and scavenging circuits. Always conduct routine performance checks when integrating cross-manufacturer components, and maintain strict documentation of system configurations to safeguard safety compliance.
What Temperature Fluctuations Will Trigger Immediate Service Requirements?
You’ll need to initiate immediate service when temperature range monitoring shows storage conditions outside 0°F-10°F (-20°C to -13°C) for liquid N2O, or if ambient temperatures exceed 25°C (77°F). For compressed gas pressure regulation, any deviation from 260-315 psi (20-25 bar) requires urgent attention. When temperatures approach 125°F in refrigerant cylinders or drop below -5.5°C in N2O/O2 mixtures above 116.5 bar, you must perform immediate system maintenance.
When Should Filter Systems Be Replaced Versus Cleaned During Maintenance?
You’ll need to replace filters immediately if you detect cracks, stiffness, or contamination during inspections. Follow routine cleaning schedules for reusable components like delivery system handpieces when they’re structurally sound. Key filter lifespan indicators include ambient N2O levels exceeding 25 ppm and scavenger system efficiency dropping below 50%. While you can clean minor connection leaks, any system failures or damaged components require immediate replacement rather than cleaning.